Review of the Plastic Periodontal and Aesthetic Surgery Course in Munich

I would like to share my impressions from the seven-part course on implants and periodontics that I attend once or twice a year. The latest course was titled "Plastic Periodontal and Esthetic Surgery" and was taught by the world-renowned periodontist Prof. Marcus Herzuler and Dr. Otto Zuhr at their educational center in Munich. They blended scientific knowledge and practical experience to provide a comprehensive overview of the indications, principles, and clinical techniques of plastic-esthetic periodontal and implant microsurgery. They focus specifically on minimal soft tissue trauma and perfect wound closure.
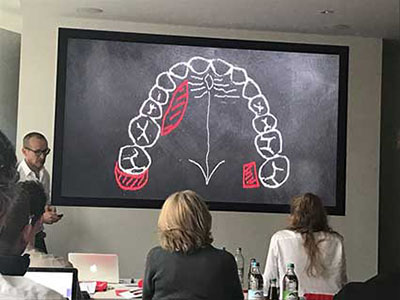
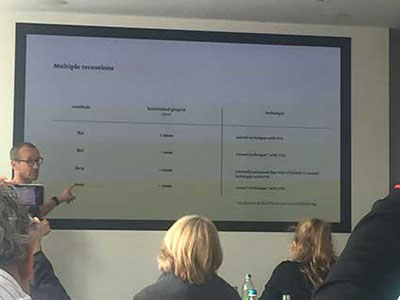
Microsurgery provides clinically relevant advantages over conventional concepts for regenerative and plastic-esthetic periodontal surgery, especially in the all-important esthetic zone. The course is both microsurgical and hands-on, and provides participants with training in the use of the operating microscope and associated microsurgical instruments. We also received training in basic microsurgical dissection, etc., on pig jaws at the Educational Center. The course is aimed at novice and experienced dentists.
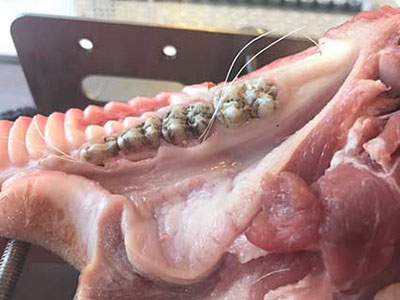
In general, microsurgery is a term describing surgery that requires high magnification such as loupes or a microscope. It is very delicate and precise and therefore involves the use of very delicate fine blades, needle, and instruments. a. Similar techniques are used in microsurgeries to facilitate surgeons who are doing microvascular surgical repairs that involve small vessels, nerves and/or other tissues. They can be used in a wide variety of surgical settings and can be used in: in various specialties. including, plastic surgery, general surgery, periodontal surgery, eye surgeries, oromaxillofacial surgery etc In the following blogs, I will further explain certain microsurgical techniques used in oral care, such as soft tissue grafting used to treat gum recession, esthetic gingivital recountering to reshape gum tissue and pontic site augmentation to treat an aftermath of trauma, usually. I hope this will help dental patients better understand the terms their dentists use and make better-informed decisions following dentist recommendations.